All of our software can be found on the lab’s GitHub page.
MOSAEC-DB – DATASET
MOSAEC-DB is a database of high-fidelity experimental MOF structures ready for simulation using improved processing and structural error analysis algorithms. It currently contains >100K structures as is updated the CSD is updated. Structural errors found in many other experimental databases have been screened for and removed.
Reference: Gibaldi, M.; Kapeliukha, A.; White, A.; Luo, J.; Mayo, R.A.; Burner, J.; Woo, T.K. “MOSAEC-DB: A comprehensive database of experimental metal-organic frameworks with verified chemical accuracy suitable for molecular simulations”, Chemical Science, 2025, 16, 4085-4100. link
Download: Currently, the database can be obtained from the CCDC website. link
ARC-MOF – DATASET
ARC-MOF is a curated database (>200K) of experimentally characterized and computer-generated MOFs ready for computation. Importantly, structural errors that are seen in many other databases have been screened for and removed in this database. The structures also include DFT derived partial atomic charges for us in simulation. ARC-MOF was featured in the journal Chemistry of Materials highlights of 2023.
Reference: Burner, J.; Luo, J.; White, A.; Mirmiran, A,; Kwon, O.; Boyd, P.G.; Maley, S.; Gibaldi, M.; Simrod, S.; Ogden, V.; Woo, T.K.* “ARC-MOF: A Diverse Database of Metal-Organic Frameworks with DFT-Derived Partial Atomic Charges and Descriptors for Machine Learning“, Chemistry of Materials, 2023, 35, 900–916. link
Download: link
HEALED SBUs for MOF construction

HEALED SBUs: are a set of SBUs (structural building units) or linkers for building MOFs that have been manually inspected for structural errors. Structural errors found in many computer generated MOF databases likely have their origin in the source SBU’s that were used.
Reference: Gibaldi, M.; Kwon, O.; White, A.; Burner, J.; Woo, T.K.* “The HEALED SBU library of chemically realistic building blocks for construction of hypothetical metal–organic frameworks”, ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 2022, 14, 43372–43386. link
Download: link
MOSAEC – Metal Oxidation State Analysis structural Error Checker
MOSAEC is the first generalized method to compute the metal oxidation states of a structure (molecular or periodic) ‘as-given’. In this way it can be used to detect structural errors when an unknown or impossible metal oxidation state is determined.
Reference: White, A.; Gibaldi, M.; Burner, J.; Mayo, R.A.; Woo, T.K.* “High structural error rates in MOF databases used in data driven workflows identified via a novel metal oxidation state-based method”, Journal of the American Chemical Society, in press. link
Download: link
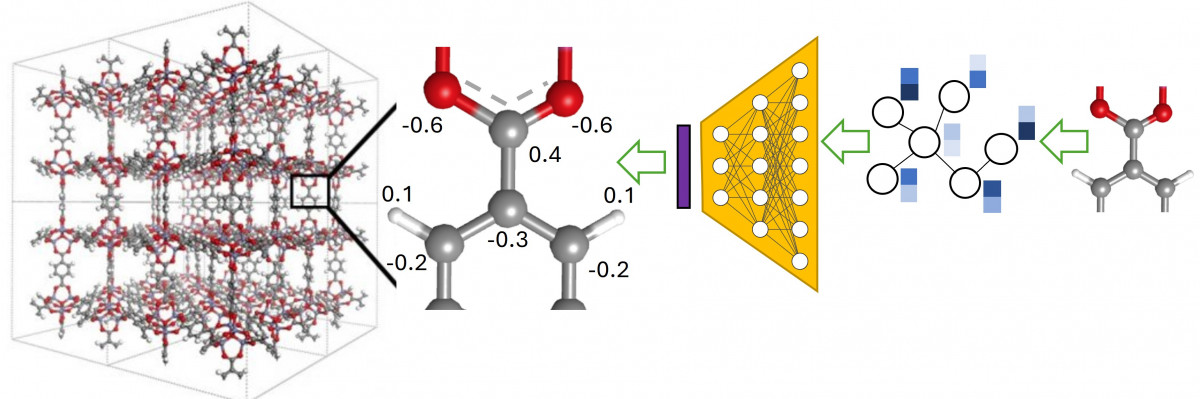
MEPO-ML
MEPO-ML is a machine learning model to rapidly generate DFT quality partial atomic charges for atomistic simulations of MOFs. MEPO-ML was trained on a dataset of over 40 million DFT computed partial atomic charges.
Reference: Luo, J.; Said, O.B.; Xie, P.; Gibaldi, M.; Burner, J.; Pereira, C.; Woo, T.K.* “MEPO-ML: a robust graph attention network model for rapid generation of partial atomic charges in metal-organic frameworks”, npj Computational Materials 2024, 10, 224. link
News: June 2025 – a new model has been trained with more experimental MOFs taken from MOSAEC-DB
Download: link
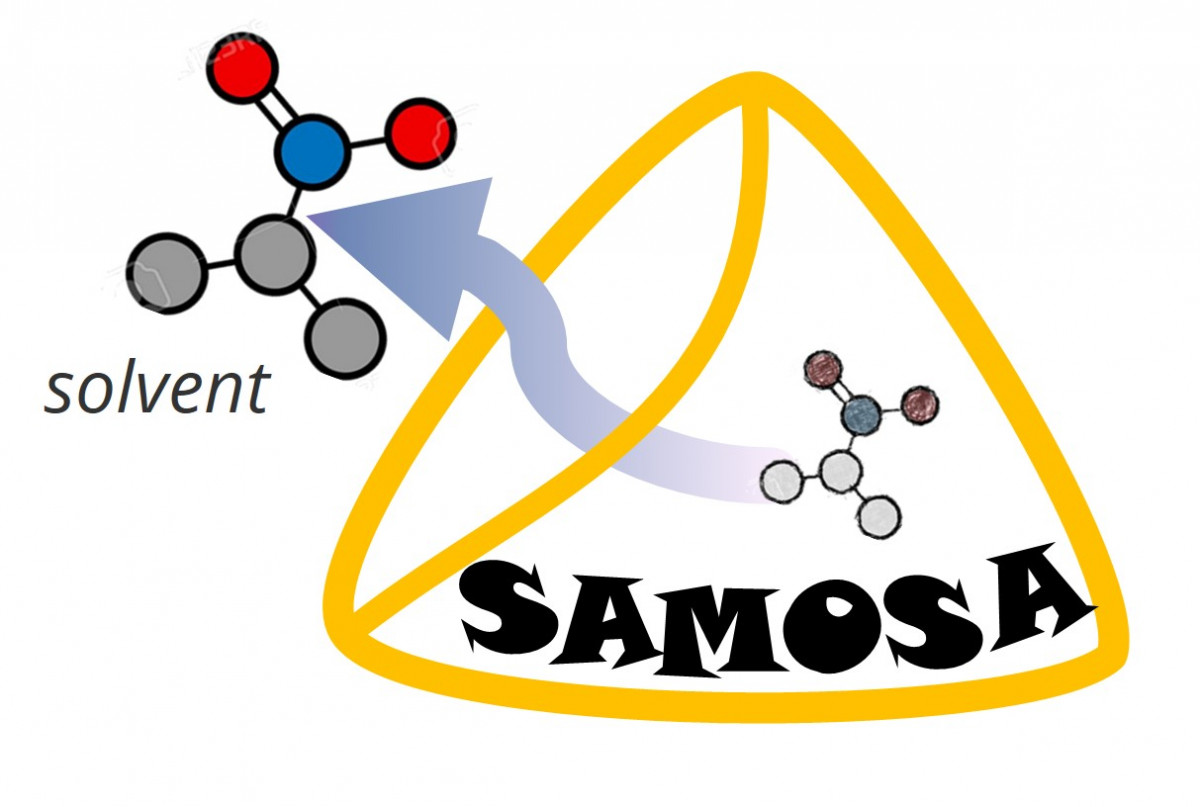
SAMOSA
SAMOSA (Structural Activation via Metal Oxidation State Analysis) is a algorithm to prepare experimental MOF crystal structures for atomistic simulation that incorporates ligand charge and metal oxidation state considerations when computationally removing solvent from the structures.
Reference: Gibaldi, M.; Kapeliukha, A.; White, A.; Woo, T.K.* “Incorporation of ligand charge and metal oxidation state considerations into the computational solvent removal and activation of experimental crystal structures preceding molecular simulation”, Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2025 65, 275-287. link
Download: link
REPEAT
REPEAT is the first method to extract electrostatic potential fitted partial atomic charges from periodic DFT calculations.
Reference: Campañá, C.; Mussard, B.; Woo, T.K.”Electrostatic Potential Derived Atomic Charges for Periodic Systems Using a Modified Error Functional: REPEAT Charges” Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation,2009, 5, 2866-2878. link
Download: link
All of our software can be found on the lab’s GitHub page.